Which Type Of Plastic Is More Suitable For Vacuum Forming And Why

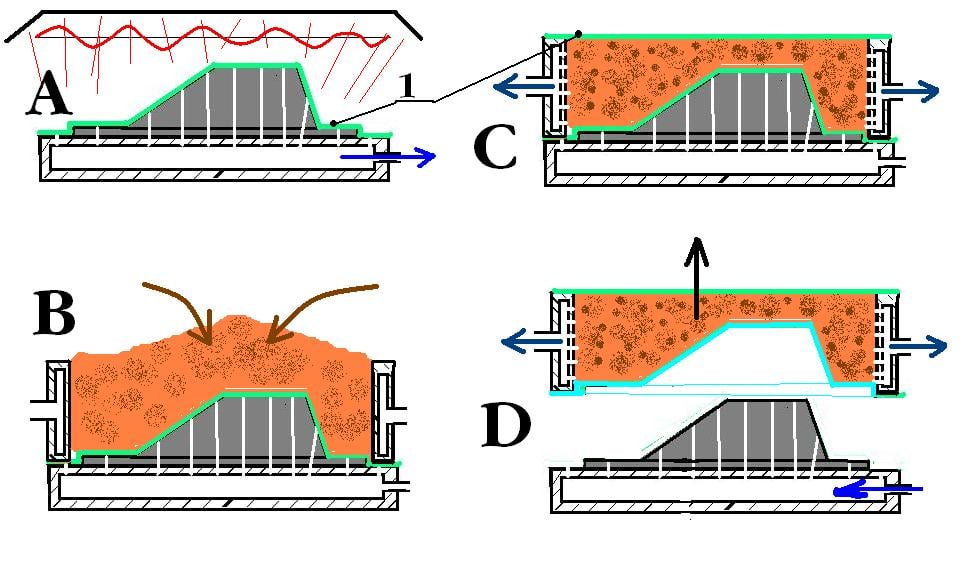
Vacuum forming is a simplified version of thermoforming where a sheet of plastic is heated to a forming temperature stretched onto a single surface mold and forced against the mold by a vacuum this process can be used to form plastic into permanent objects such as turnpike signs and protective covers.
Which type of plastic is more suitable for vacuum forming and why. A vacuum is applied sucking the sheet into the mould. In our recent blog post giving an introduction to the vacuum forming process we covered each stage of how plastic products are made using vacuum forming in this post we will be giving an overview of which plastic materials are suitable for vacuum forming and the individual characteristics of each. Materials for use in vacuum are materials that show very low rates of outgassing in vacuum and where applicable are tolerant to bake out temperatures. This is a type of vacuum forming where thin or thick gauge plastic sheet is placed over a die heated to a temperature that allows the material to become pliable then is stretched over the surface of the die while vacuum pressure pulls the sheet down and into its final shape.
The process involves heating a plastic sheet until soft and then draping it over a mould. The requirements grow increasingly stringent with the desired degree of vacuum to be achieved in the vacuum chamber the materials can produce gas by several mechanisms. Thermoforming is one of the oldest and most common methods of processing plastic materials. Normally draft angles are present in the design of the mold a recommended minimum of 3.
The sheet is then ejected from the mould.